Project carried out as a member of the Stratos V team at DARE, whose aim was to design and build a liquid propellant reusable rocket.
Project Summary
Independently developed a comprehensive Python-based engineering tool to automate the preliminary design and sizing of the Stratos V rocket propellant tanks. The software serves as a critical bridge between system requirements and detailed design, allowing for the rapid generation, validation, and optimization of tank geometries before committing to time-intensive Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and prototype testing.
Software Architecture
The tool utilizes a modular architecture to ensure flexibility and ease of use, divided into distinct modules: databases (materials, fluids, loads), formulas (stress and buckling calculations), handlers (configuration management), and section definitions.
- User Interface: The tool features an accessible interface where users input ranges for wall thicknesses, radii, pressures, and materials, allowing the tool to iterate through thousands of potential designs automatically.
- Visualization: Integrated visualization handlers generate immediate 2D representations of the tank configuration and plot stress distributions along the tank geometry.
The following diagram illustrates the tool’s execution workflow:
graph LR A["<b>Configuration Input</b><br/>(Geometry, Loads, Materials)"] --> B["<b>Set Generation</b><br/>(Iterative Design Creation)"] B --> C["<b>Validation Filters</b><br/>(Failure Mode Checks)"] C --> D["<b>Optimization & Analysis</b><br/>(Selection & Visualization)"]
Geometry & Structural Support
The tool supports complex geometric definitions to ensure high-fidelity modeling during the preliminary phase:
- Dome Profiles: Validates and sizes multiple dome geometries, including Hemispherical, Semi-ellipsoidal, and Cassinian shapes. It calculates specific stress distributions for each profile, specifically monitoring for compressive hoop stresses in flatter domes (e.g., Cassinian shapes with high affine transformation factors) which could induce buckling.
- Cylindrical & Skirt Sections: Models the main tank body as a thin-walled cylinder. It supports advanced skirt designs, including options for Unstiffened, Ring-stringer, and Isogrid stiffening elements. The tool calculates the specific elastic constants for these stiffened orthotropic shells to optimize for weight while maximizing buckling resistance.
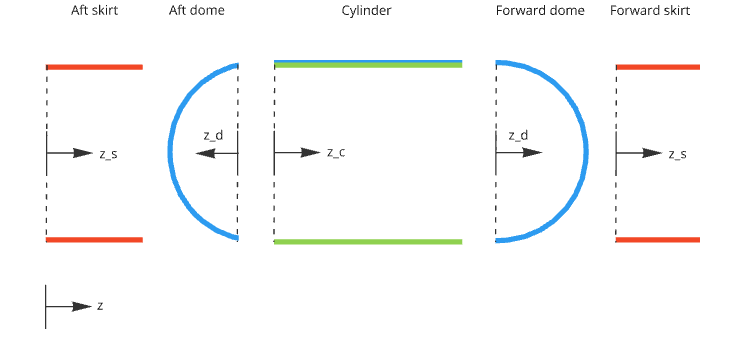
Tank component breakdown showing coordinate systems for skirts, domes, and cylinder sections.
Physics & Failure Analysis
The core function of the tool is to validate configurations against specific failure modes. It accounts for a comprehensive load case set including compressive axial forces, bending moments, and internal pressures. Both analytical and empirical relations from a wide range of sources are used here. Key calculations include:
- Stress Analysis: Calculates Hoop and Meridional stresses across the dome and cylinder, validating against material yield strength using the Von Mises yield criterion.
- Buckling Analysis: Performs critical buckling load analysis for both axial and bending loads. It applies knockdown factors to account for shell imperfections and calculates load interaction curves combining axial and bending loads.
- Stiffness & Vibration: Estimates structural stiffness and checks bending modes using Donnell’s natural frequency formulation to ensure natural frequencies remain above critical thresholds.
- Thermal Analysis: Simulates temperature profiles for the cylinder, skirt, and fluid over time to ensure structural integrity under cryogenic conditions.
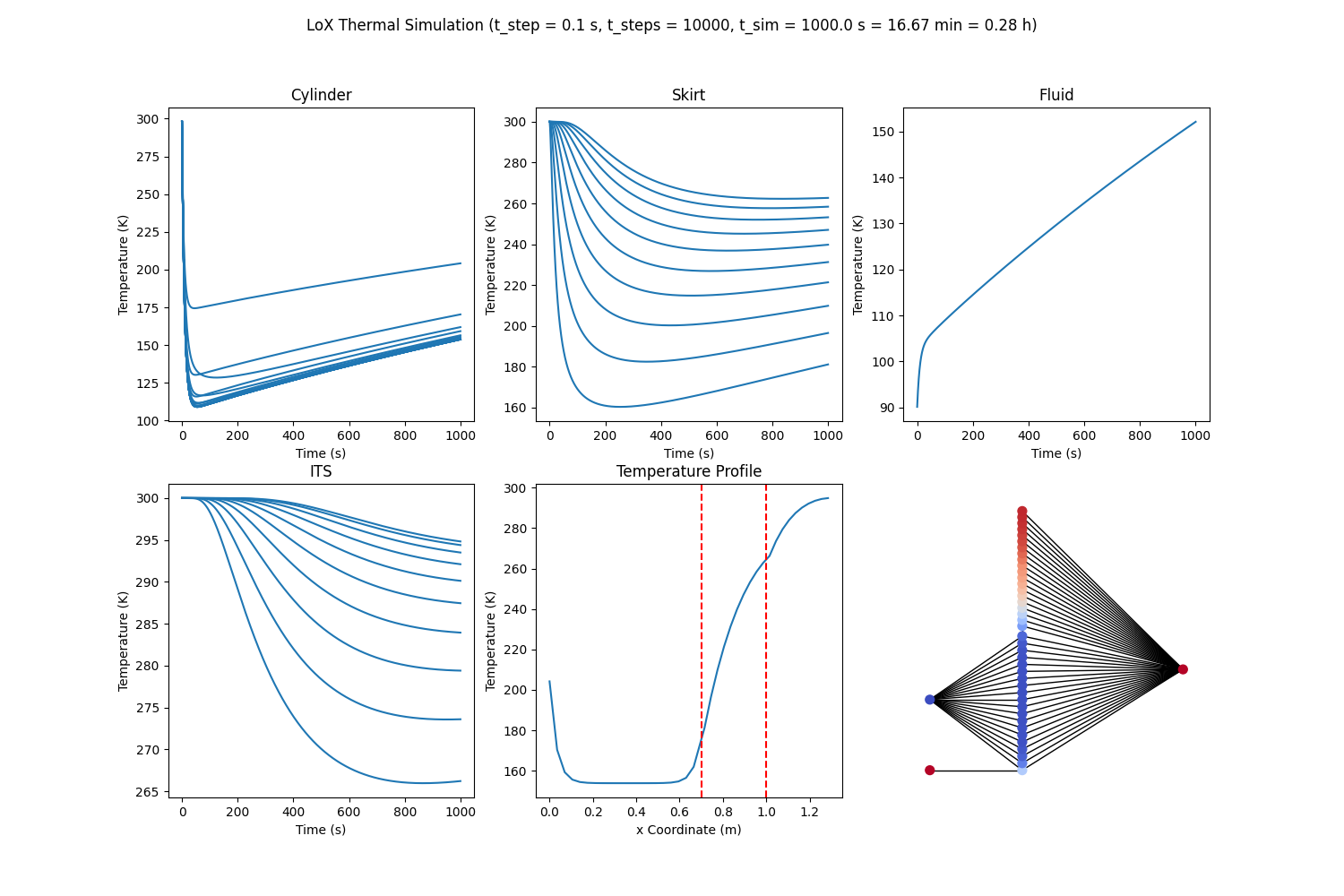
Dummy transient thermal simulation output showing temperature evolution of LOx tank components and fluid over a flight duration.
Optimization & FEA Integration
- Rapid Iteration: The tool generates a set of potential configurations based on the input iterables, filters them through “validator” functions (checking for yielding, buckling, and geometric constraints), and automatically sorts them to identify the lightest possible design.
- FEA Validation: Acts as a rapid validation step to define the preliminary design parameters (thickness, radius, height). These optimized outputs are then used as the baseline for detailed Finite Element Modeling (FEM) and simulations, significantly reducing the iteration time required in complex simulation environments.
Example Output
The tool provides both graphical visualizations and detailed tabular data to summarize the final optimized design. This immediate feedback loop allows for rapid assessment of geometric feasibility before proceeding to detailed manufacturing planning.
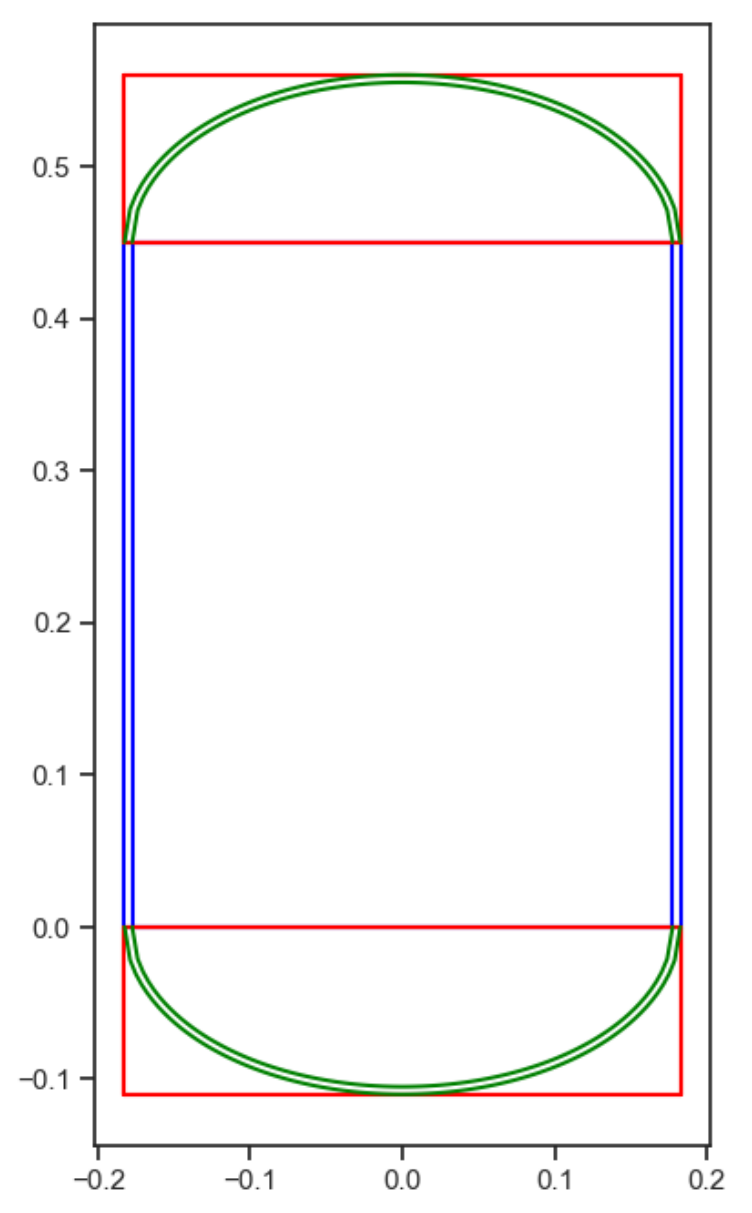
Dummy tank geometry representation.
Component Breakdown
The tool generates a granular breakdown of the tank assembly, isolating the cylinder, domes, and skirts. The following table provides the specific physical parameters required for manufacturing (such as wall thickness and height) and precise mass estimates for each individual component.
| Parameter \ Section | forward_dome | aft_dome | cylinder | forward_skirt | aft_skirt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| height m | 0.15 | 0.15 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| inner_diameter m | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.508 | 0.508 |
| inner_volume m³ | 0.0152 | 0.0152 | 0.2356 | 0.0304 | 0.0304 |
| thickness m | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| mass kg | 1.45 | 1.45 | 12.85 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| material | 7075-T6 | 7075-T6 | 7075-T6 | 7075-T6 | 7075-T6 |
| type | hemispherical | hemispherical | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Validation Summary
The validation output acts as a compliance matrix, confirming that the optimized geometry meets all structural and functional requirements. It explicitly lists the status of critical failure modes (such as hoop stress collapse, axial buckling, and bending interactions) alongside functional constraints like maximum mass and minimum ullage volume.
| Validator | Parameter | Value | Unit | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| max_mass | configuration mass | 17.45 | kg | passed |
| ullage | inner volume | 0.266 | m³ | passed |
| cylinder_hoop_collapse | hoop stress | 3.10E+08 | Pa | passed |
| cylinder_axial_buckling | critical axial buckling load | 450200 | N | passed |
| cylinder_bending_buckling | critical bending buckling load | 52000 | Nm | passed |
| skirt_load_interaction | axial/bending interaction | 0.82 | N/A | passed |
| dome_yielding | dome yielding | N/A | N/A | passed |